

Hi, I’m TestprepKart.
Your Partner In Exam Preparation

Navigating the final moments before the Class 11 CBSE exams can be crucial and challenging. A comprehensive set of last-minute preparation resources has been curated to aid students in this pivotal period. These resources encompass condensed study guides, concise notes, quick revision sheets, and practice question banks.
Tailored to the CBSE Class 11th syllabus, these materials aim to streamline revision, reinforce key concepts, and enhance exam readiness. Designed for quick assimilation, these resources serve as invaluable tools for students seeking to optimize their study time and perform confidently in their upcoming examinations.
Maths Last minutes preparation Notes:
| CBSE Class11 Maths Notes | Document Notes | Videos Notes |
|
Chapter 1. Sets Introduction, Sets and their Representations, The Empty Set, Finite and Infinite Sets, Equal Sets, Subsets, Universal Sets, Venn Diagrams, Operations on Sets, Complement of a Set |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 2. Relations and Functions Introduction, Cartesian Product of Sets, Relations, Functions |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 3. Trigonometric Functions Introduction, Angles, Trigonometric Functions, Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 4. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Introduction, Complex Numbers, Algebra of Complex Numbers, The Modulus and the Conjugate of a Complex Number, Argand Plane and Polar Representation |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 5. Linear Inequalities Introduction, Inequalities, Algebraic Solutions of Linear Inequalities in and their Graphical Representation One Variable |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 6. Permutations and Combinations Introduction, Fundamental Principle of Counting, Permutations, Combinations |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 7. Binomial Theorem Introduction, Binomial Theorem for Positive Integral Indices |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 8. Sequences and Series Introduction, Sequences, Series, Geometric Progression (G.P.), Relationship Between A.M. and G.M. |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 9. Straight Lines Introduction, Slope of a Line, Various Forms of the Equation of a Line, Distance of a Point From a Line |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 10. Conic Sections Introduction, Sections of a Cone, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 11. Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry Introduction, Coordinate Axes and Coordinate Planes in Three-Dimensional Space, Coordinates of a Point in Space, Distance between Two Points |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 12. Limits and Derivatives Introduction, Intuitive Idea of Derivatives, Limits, Limits of Trigonometric Functions , Derivatives |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 13. Statistics Introduction, Measures of Dispersion, Range, Mean Deviation, Variance and Standard Deviation |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 14. Probability Event, Axiomatic Approach to Probability |
 |
 |
Empower your last-minute math revision for CBSE Class 11 with our concise preparation notes. Key formulas, tips, and practice questions tailored for quick grasp. Boost your confidence and ace the exam effortlessly.
Physics minutes preparation Notes :
| CBSE Class11 Physics Notes | Document Notes | Videos Notes |
|
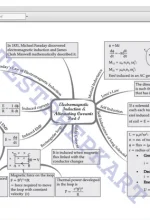
Chapter 1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS Introduction, The international system of units, Significant figures, Dimensions of physical quantities, Dimensional formulae and dimensional equations, Dimensional analysis and its applications |
 |
 |
|
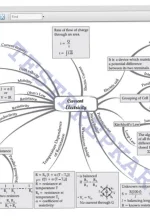
Chapter 2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE Introduction, Instantaneous velocity and speed, Acceleration, Kinematic equations for uniformly accelerated motion |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 3: MOTION IN A PLANE Introduction, Scalars and vectors, Multiplication of vectors by real numbers, Addition and subtraction of vectors – graphical method, Resolution of vectors, Vector addition – analytical method, Motion in a plane, Motion in a plane with constant acceleration, Projectile motion, Uniform circular motion |
 |
 |
|
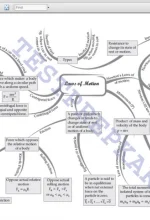
Chapter 4: LAWS OF MOTION Introduction, Aristotle’s fallacy, The law of inertia, Newton’s first law of motion, Newton’s second law of motion, Newton’s third law of motion, Conservation of momentum, Equilibrium of a particle, Common forces in mechanics, Circular motion, Solving problems in mechanics |
 |
 |
|
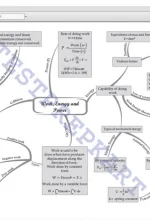
Chapter 5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER Introduction, Notions of work and kinetic energy: The work-energy theorem, Work, Kinetic energy, Work done by a variable force, The concept of potential energy, The conservation of mechanical energy, The potential energy of a spring, Power, Collisions |
 |
 |
|
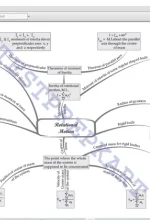
Chapter 6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION Introduction, Centre of mass, Centre of mass, The motion of the center of mass, Vector product of two vectors, Angular velocity and its relation with linear velocity, Torque and angular momentum, Equilibrium of a rigid body, Moment of inertia, Kinematics of rotational motion about a fixed axis, Dynamics of rotational motion about a fixed axis, Angular momentum in case of rotations about a fixed axis |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 7: GRAVITATION Introduction, Kepler’s laws, The universal law of gravitation, The gravitational constant, Acceleration due to the gravity of the earth, Acceleration due to gravity below and above the surface of the earth, Gravitational potential energy, Escape speed, Earth satellites, Energy of an orbiting satellite |
 |
 |
|
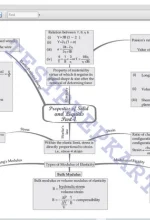
Chapter 8: Mechanical Properties of Solids Introduction, Stress and strain, Hooke’s law, Stress-strain curve, Elastic moduli, Applications of elastic behavior of materials |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 9: Mechanical Properties of Fluids Introduction, Pressure, Streamline flow, Bernoulli’s principle, Viscosity, Surface tension |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 10: Thermal Properties of Matter Introduction, Temperature and heat, Measurement of temperature, gas equation and absolute temperature, Thermal expansion, Specific heat capacity Calorimetry, Change of state, Heat transfer, Newton’s law of cooling |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 11: Thermodynamics Introduction, Thermal equilibrium, Zeroth law of thermodynamics, Heat, internal energy, and work, The first law of thermodynamics, Specific heat capacity, Thermodynamic state variables and equation of state, Thermodynamic processes, Second law of thermodynamics, Reversible and irreversible processes, Carnot engine |
 |
 |
|
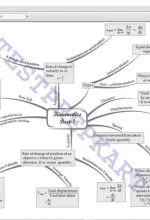
Chapter 12: Kinetic Theory Introduction, Molecular nature of matter, Behaviour of gases, Kinetic theory of an ideal gas, Law of equipartition of energy, Specific heat capacity, Mean free path |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 13: Oscillations Introduction, Periodic and oscillatory motions, Simple harmonic motion, Simple harmonic motion and uniform circular motion, Velocity and acceleration in simple harmonic motion, Energy in simple harmonic motion, The Simple Pendulum |
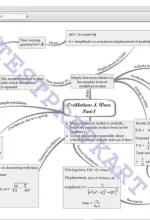 |
 |
|
Chapter 14: Waves Introduction, Transverse and longitudinal waves, Displacement relation in a progressive wave, The speed of a traveling wave, The principle of superposition of waves, Reflection of waves, Beats |
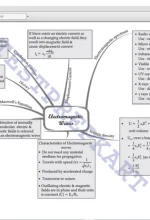 |
 |
Master physics effortlessly with our last-minute preparation notes for CBSE Class 11. Condensed insights, vital formulas, and strategic tips to optimize your revision. Elevate your confidence and tackle the exam with precision. Shine in physics.
Chemistry Last minutes preparation Notes :
| CBSE Class11 Chemistry Notes | Document Notes | Videos Notes |
|
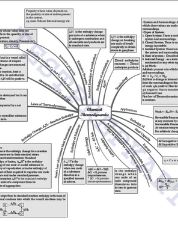
Chapter: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Importance of Chemistry, Nature of Matter, Properties of Matter and Their Measurement, Uncertainty in Measurement, Laws of Chemical Combinations Dalton’s Atomic Theory, Atomic and Molecular Masses, Mole Concept and Molar Masses, Percentage Composition, Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations |
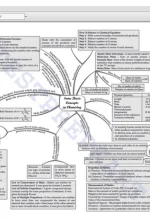 |
 |
|
Chapter 2: Structure of Atom Discovery of Sub-atomic Particles, Atomic Models, Developments Leading to Bohr’s Model of Atom, Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom, Towards the Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom, Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom |
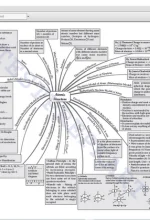 |
 |
|
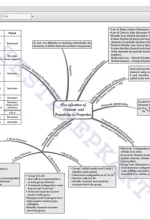
Chapter 3: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Why do we Need to Classify Elements?, Genesis of Periodic Classification, Modern Periodic Law and the Present Form of the Periodic Table, Nomenclature of Elements with Atomic Numbers, Electronic Configurations of Elements and the Periodic Table, Electronic Configurations and Types of Elements: 82 s-, p-, d-, f- Blocks, Periodic Trends in Properties of Elements
|
 |
 |
|
Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Kössel-Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Bond Parameters, The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Hybridization, Molecular Orbital Theory, Bonding in Some Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules, Hydrogen Bonding |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 5: Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Terms, Applications, Measurement of ∆U and ∆H: Calorimetry, Enthalpy Change, ∆rH of a Reaction – Reaction Enthalpy, Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions, Spontaneity, Gibbs Energy Change and Equilibrium |
 |
 |
|
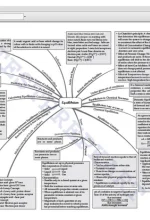
Chapter 6: Equilibrium Equilibrium in Physical Processes, Equilibrium in Chemical Processes – Dynamic Equilibrium, Law of Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constant, Homogeneous Equilibria, Heterogeneous Equilibria, Applications of Equilibrium Constants, Factors Affecting Equilibria, Ionic Equilibrium in Solution, Acids, Bases, and Salts, Ionization of Acids and Bases, Buffer Solutions, Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts |
 |
 |
|
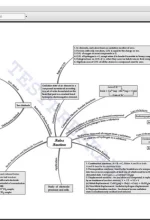
Chapter 7: Redox Reactions Classical Idea of Redox Reactions-Oxidation and Reduction Reactions, Redox Reactions in Terms of Electron Transfer Reactions, Oxidation Number, Redox Reactions, and Electrode Processes |
 |
 |
|
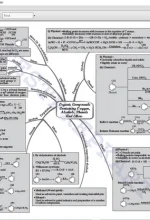
Chapter 8: Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques General Introduction, Tetravalence of Carbon: Shapes of Organic Compounds Structural Representations of Organic Compounds, Classification of Organic Compounds, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, Isomerism, Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanism, Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds, Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds, Quantitative Analysis |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 9: Hydrocarbons Classification, Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Aromatic Hydrocarbon, Carcinogenicity and Toxicity |
 |
 |
Elevate your CBSE Class 11 Chemistry revision with our last-minute preparation notes. Streamlined content, essential concepts, and effective tips for quick mastery. Gear up for success and approach the exam with confidence. Ace your Chemistry paper effortlessly.
Biology Last minutes preparation Notes :
| CBSE Class11 Biology Notes | Document Notes | Videos Notes |
|
Chapter 1: The Living World Biodiversity, Need for classification; three domains of life, Biodiversity |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 2: Biological Classification Five kingdom classification, Salient features and classification of Monera, Protista, and Fungi into major groups |
 |
 |
|
Chapter-3: Plant Kingdom Classification of plants into major groups, Salient and distinguishing features, A few examples of Algae are Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, and Gymnospermae |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 4: Animal Kingdom Salient features and classification of animals, Non-chordates up to phyla level and chordates up to class level, (salient features and a few examples of each category). |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 5: Morphology of Flowering Plants Morphology of different parts of flowering plants: root, stem, leaf, inflorescence, flower, fruit, and seed, Description of the family Solanaceae |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants Anatomy and functions of tissue systems in dicots and monocots. |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 7: Structural Organisation in Animals Morphology, Anatomy, and functions of different systems |
 |
 |
|
Chapter-8: Cell-The Unit of Life Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life, structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, Plant cells and animal cells, Cell envelope, Cell membrane, cell wall, Cell organelles – structure and function, The endomembrane system, The endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, Lysosomes, vacuoles, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Plastids, Microbodies, Cytoskeleton, Cilia, flagella, Centrioles (ultrastructure and function), Nucleus |
 |
 |
|
Chapter-9: Biomolecules Chemical constituents of living cells: biomolecules, structure, and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, Enzyme – types, properties, Enzyme action. (Topics excluded: Nature of Bond Linking Monomers in a Polymer, Dynamic State of Body Constituents – Concept of Metabolism, Metabolic Basis of Living, The Living State)
|
 |
 |
|
Chapter 10: Cell Cycle, Cell Division Cell Cycle, Cell Division Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, and their significance |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Photosynthesis as a means of autotrophic nutrition, Site of photosynthesis, pigments involved in photosynthesis (elementary idea), Photochemical and biosynthetic phases of photosynthesis, Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation, Chemiosmotic hypothesis; photorespiration, C3 and C4 pathways, Factors affecting photosynthesis |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 14: Respiration in Plants Exchange of gases, Cellular respiration – glycolysis, fermentation (anaerobic), TCA cycle, and electron transport system (aerobic), Energy relations – number of ATP molecules generated, amphibolic pathways, Respiratory quotient
|
 |
 |
|
Chapter 15: Plant – Growth and Development Seed germination, Phases of plant growth and plant growth rate, Conditions of growth, Differentiation, differentiation, and differentiation, The sequence of developmental processes in a plant cell, Growth regulators – auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, ethylene, ABA |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases Respiratory organs in animals (recall only), Respiratory system in humans, mechanism of breathing and its regulation in humans – Disorders related to respiration – asthma, emphysema, occupational respiratory disorders |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 18: Body Fluids and Circulation Composition of the blood, blood groups, coagulation of blood, Composition of lymph and its function, Human circulatory system – Structure of human heart and blood vessels, Cardiac cycle, cardiac output, ECG, Double circulation, Regulation of cardiac activity, Disorders of the circulatory system – hypertension, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, heart failure
|
 |
 |
|
Chapter 19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination Modes of excretion – ammonotelism, ureotelism, uricotelism, Human excretory system –structure and function, Urine formation, osmoregulation, Regulation of kidney function – renin-angiotensin, atrial natriuretic factor, ADH, and diabetes insipidus, Role of other organs in excretion, Disorders – uremia, renal failure, renal calculi, nephritis, Dialysis and artificial kidney, a kidney transplant |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Types of movement – ciliary, flagellar, muscular; skeletal muscle, contractile proteins, and muscle contraction Skeletal system and its functions, Joints, Disorders of muscular and skeletal systems – myasthenia gravis, |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 21: Neural Control and Coordination Neuron and nerves, The nervous system in humans – central nervous system; Generation and conduction of nerve impulse |
 |
 |
|
Chapter 22: Chemical Coordination and Integration Endocrine glands and hormones, Human endocrine system – hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads, Mechanism of hormone action (elementary idea), Role of hormones as messengers and regulators, hypo – and hyperactivity, Related disorders; Dwarfism, acromegaly, diabetes, and Addison's disease, cretinism, goiter, exophthalmic goiter |
 |
 |
Optimize your CBSE Class 11 Biology review with our last-minute preparation notes. Compact summaries, crucial concepts, and strategic tips for swift understanding. Bolster your readiness and approach the exam with assurance. Excel in Biology effortlessly.
Q1. Why is last-minute preparation important for Class 11 exams?
Answer. Last-minute preparation helps reinforce key concepts, boost confidence, and refine exam strategies, maximizing performance.
Q2. How should I prioritize subjects during last-minute study sessions?
Answer. Prioritize subjects based on your proficiency and the exam schedule. Allocate more time to challenging topics while reviewing familiar ones efficiently.
Q3. Are there specific resources tailored for last-minute preparation?
Answer. Yes, our last-minute preparation notes offer concise summaries, important formulas, and quick tips designed to facilitate efficient revision.
Q4. How can I use the last minutes before the exam wisely?
Answer. Glance through your notes, focus on key points, and avoid new information. Relax, visualize success, and enter the exam hall with confidence.
Q5. What if I haven't covered all the topics during last-minute preparation?
Answer. Prioritize remaining topics based on weightage and relevance. Focus on understanding core concepts rather than attempting to cover everything. Confidence in mastered topics matters most.
Copyright © 2024 CounselKart Educational Services Pvt. Ltd.. All Rights Reserved


Post a Comment