CBSE Class 11 Atomic and Molecular Masses Detail & Preparation Downloads
In the intricate world of chemistry, the concepts of atomic and molecular masses serve as fundamental pillars, unlocking the mysteries of matter on both microscopic and macroscopic scales. Atomic mass represents the mass of an individual atom, intricately tied to the composition of its subatomic particles. On the other hand, molecular mass delves into the cumulative weight of molecules, encapsulating the combined masses of constituent atoms.
Atomic and Molecular Masses Unveiled in CBSE NCERT Download
Atomic and Molecular Masses
Atomic mass pertains to the average mass of an atom, encompassing protons, neutrons, and electrons. It is expressed in atomic mass units (u). Molecular mass, on the other hand, delves into the combined mass of atoms within a molecule. Calculated by summing the atomic masses of its constituent elements, the molecular mass is crucial for stoichiometry, guiding reactions, and proportions in chemical processes. Both atomic and molecular masses play pivotal roles in deciphering the quantitative intricacies of the microscopic realm, shaping our understanding of the composition and behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular levels.
What is Atomic Mass?
Atomic mass refers to the average mass of an atom of a chemical element, expressed in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu). It takes into account the masses of the atom's constituent subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The atomic mass is typically found on the periodic table beneath the chemical symbol of each element. It is an average value because most elements exist as a mixture of isotopes, each with a slightly different mass due to variations in the number of neutrons.
Atomic Mass of Element
To find the atomic mass of an element, you typically refer to the periodic table. The atomic mass is listed beneath the chemical symbol of the element. It is given in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu). The value is an average atomic mass that takes into account the abundances of the element's isotopes.
For example, let's consider the element carbon:
- The atomic number of carbon is 6.
- The atomic mass of carbon, as found on the periodic table, is approximately 12.01 u.
What is Molecular Mass?
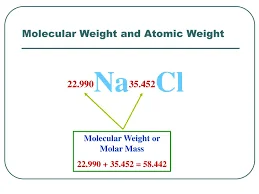
Molecular mass refers to the mass of a single molecule and is expressed in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu). It is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in a molecule. The molecular mass is also sometimes called molecular weight.
Key Points on Atomic and Molecular Masses:
Atomic Mass:
- The average mass of an atom of a specific element.
- Measured in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu).
- Found on the periodic table below the chemical symbol.
- Considers the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Represents an average value due to isotopic variations.
Molecular Mass:
- Mass of a single molecule.
- Measured in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu).
- Calculated by summing atomic masses of constituent atoms.
- Formula: =M∑(mass of atom×number of atoms)M=∑(mass of atom×number of atoms).
- Facilitates stoichiometry in chemical reactions.
Unit of Measurement:
- Both are expressed in atomic mass units (u) or unified atomic mass units (amu).
Role in Chemistry:
- Crucial for understanding element composition and isotopic variations.
- Essential for determining mass relationships in compounds.
Average Values:
- Atomic mass considers isotopic abundances.
- Molecular mass is the sum of average atomic masses.
Periodic Table Information:
- Atomic masses are listed on the periodic table.
- Molecular masses are calculated based on atomic masses.
Application in Chemistry:
- Fundamental in quantitative chemistry.
- Guides stoichiometric calculations in chemical reactions

CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
|
1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary |
View Page / Download |
|
2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books |
View Page / Download |
|
3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions |
View Page / Download |
|
4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar |
View Page / Download |
|
5. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers |
View Page / Download |
|
6. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank |
View Page / Download |
|
7. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes |
View Page / Download |
|
8. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources |
View Page / Download |
|
9. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books |
View Page / Download |
|
10. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet |
View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES:
Q1: What is atomic mass?
Answer. Atomic mass is the mass of an atom, typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu). It represents the average mass of an element's atoms, taking into account the different isotopes and their abundances.
Q2: How is atomic mass calculated?
Answer. Atomic mass is calculated by taking the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element, based on their relative abundances.
Q3: What is molecular mass?
Answer. Molecular mass, also known as molecular weight, is the mass of a molecule. It is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule, measured in atomic mass units (amu) or grams per mole.
Q4: How is atomic mass different from molecular mass?
Answer. Atomic mass refers to the mass of an individual atom, whereas molecular mass refers to the mass of a molecule, which is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in that molecule.
Q5: Why is atomic and molecular mass important in chemistry?
Answer. Atomic and molecular mass are crucial in chemistry for various reasons:
- Stoichiometry: They are essential for calculating the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions.
- Empirical and Molecular Formulas: Determining the formulas of compounds requires knowledge of atomic and molecular masses.
- Limiting Reactant Calculations: Atomic and molecular masses are used to identify limiting reactants and calculate yields in chemical reactions.
- Understanding Composition: They provide insight into the composition of substances, aiding in the understanding of their properties and behavior.

| CBSE CLASS 11th Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| > Importance of Chemistry |
| > Nature of Matter |
| > Properties of Matter and their Measurement |
| > Uncertainly in Measurement |
| > Laws of Chemical Combinations |
| > Dalton's Atomic Theory |
| > Mole Concept and Molar Masses |
| > Percentage composition |
| > Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| CBSE Class 11 Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |