CBSE Class 11 uncertainty in Measurement Detail & Preparation Downloads
We will explore the fundamental principles of uncertainty, dissecting its various sources and manifestations. From the statistical intricacies that underpin uncertainty calculations to real-world applications across diverse fields, join us as we navigate the tapestry of uncertainty, unraveling its threads one measurement at a time. Whether you are a seasoned scientist, an aspiring researcher, or simply someone intrigued by the precision behind the numbers, this blog seeks to demystify the complexities that shroud our measurements.
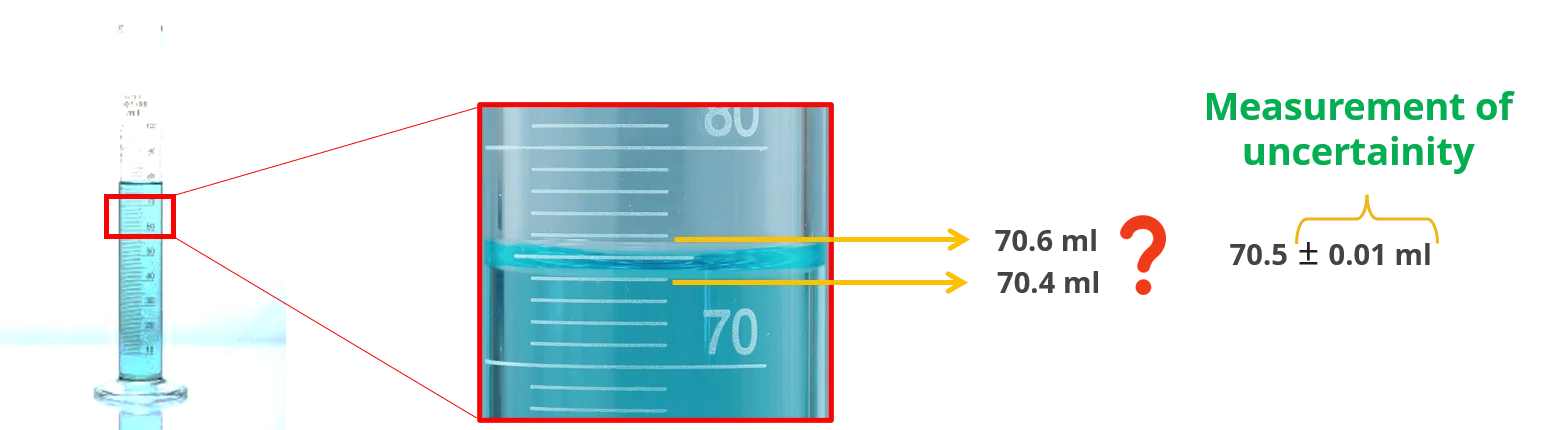
Understanding Uncertainty in Measurement with CBSE NCERT Download
Understanding Uncertainty in Measurement
Welcome to the intriguing world of scientific measurements, where precision meets its constant companion – uncertainty. As budding scientists in the eleventh grade, it's time to unravel the mystery behind the numbers and explore the fascinating concept of uncertainty in measurement.
What is Uncertainty?
Imagine trying to measure the length of a table with a ruler. You might get a slightly different result each time you measure. That variation, or doubt in the measurement, is what we call uncertainty. It's like a tiny cloud of doubt that follows every measurement, reminding us that there's a range within which our true value might lie.
Sources of Uncertainty
Instrumental Limitations: Even the most advanced tools have their limits. Think of a weighing scale; it might not show the exact weight due to its precision constraints.
Human Error: Yes, we're not perfect! Small mistakes can creep in during the measurement process, influencing our results.
Environmental Factors: Changes in temperature, humidity, or other environmental conditions can affect measurements.
Types of Uncertainty
Systematic Uncertainty: This type arises from consistent errors in our measurement process. It's like a persistent hitch that nudges our results in a particular direction.
Random Uncertainty: Unpredictable factors introduce variability. Random uncertainty is like the playful dance of particles, making each measurement a tad different.
Why Does It Matter?
Understanding uncertainty is crucial for honest and reliable science. It's not about doubting our measurements but acknowledging the range of possibilities. Precision becomes meaningful when we know the boundaries within which our measurements are reliable.

CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
|
1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary |
View Page / Download |
|
2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books |
View Page / Download |
|
3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions |
View Page / Download |
|
4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar |
View Page / Download |
|
5. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers |
View Page / Download |
|
6. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank |
View Page / Download |
|
7. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes |
View Page / Download |
|
8. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources |
View Page / Download |
|
9. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books |
View Page / Download |
|
10. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet |
View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES:
Q1. What is uncertainty in measurement?
Answer. Uncertainty in measurement refers to the lack of perfect precision in determining the value of a quantity. It acknowledges the inherent limitations and potential errors in any measurement due to the precision of the measuring instrument and other factors.
Q2. Why is uncertainty important in science?
Answer. Uncertainty is crucial in science because it provides a measure of the reliability of a measurement. Recognizing and quantifying uncertainty helps scientists assess the credibility and validity of experimental results, make informed decisions, and communicate the precision of their findings.
Q3. What is systematic uncertainty?
Answer. Systematic uncertainty, also known as systematic error, is a type of uncertainty that arises from consistent and repeatable sources, leading to a consistent deviation of measurements from the true value. It is not random and can often be attributed to flaws in the experimental setup, calibration, or measurement technique.
Q4. How is uncertainty expressed?
Answer. Uncertainty is often expressed using error bars, confidence intervals, or standard deviation. The value is typically reported with a margin of error, indicating the range within which the true value is likely to lie.
Q5. How can we reduce uncertainty in measurements?
Answer. To reduce uncertainty in measurements, one can:
- Use more precise instruments with smaller increments.
- Repeat measurements and calculate the average to minimize random errors.
- Calibrate instruments regularly to ensure accuracy.
- Minimize systematic errors by carefully designing and controlling experiments.
- Consider and account for all sources of uncertainty in the measurement process.

| CBSE CLASS 11th Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| > Importance of Chemistry |
| > Nature of Matter |
| > Properties of Matter and their Measurement |
| > Laws of Chemical Combinations |
| > Dalton's Atomic Theory |
| > Atomic and molecular Masses |
| > Mole Concept and Molar Masses |
| > Percentage composition |
| > Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| CBSE Class 11 Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |