CBSE Class 11 Nature of Matter Detail & Preparation Downloads
Matter, in its myriad forms, is the substance that occupies space and possesses mass, playing a central role in the tapestry of existence. From the vast cosmic structures to the smallest particles imperceptible to the naked eye, understanding the nature of matter is a journey that spans the realms of the macroscopic and the microscopic, probing the essence of reality itself. In this exploration, we delve into the rich tapestry of the physical world, unraveling the secrets that govern the behavior, composition, and interactions of matter at its most fundamental level. Join us on a voyage through the realms of atoms, molecules, and the forces that bind them together, as we embark on a fascinating journey to comprehend the nature of matter and the profound implications it holds for our comprehension of the universe.
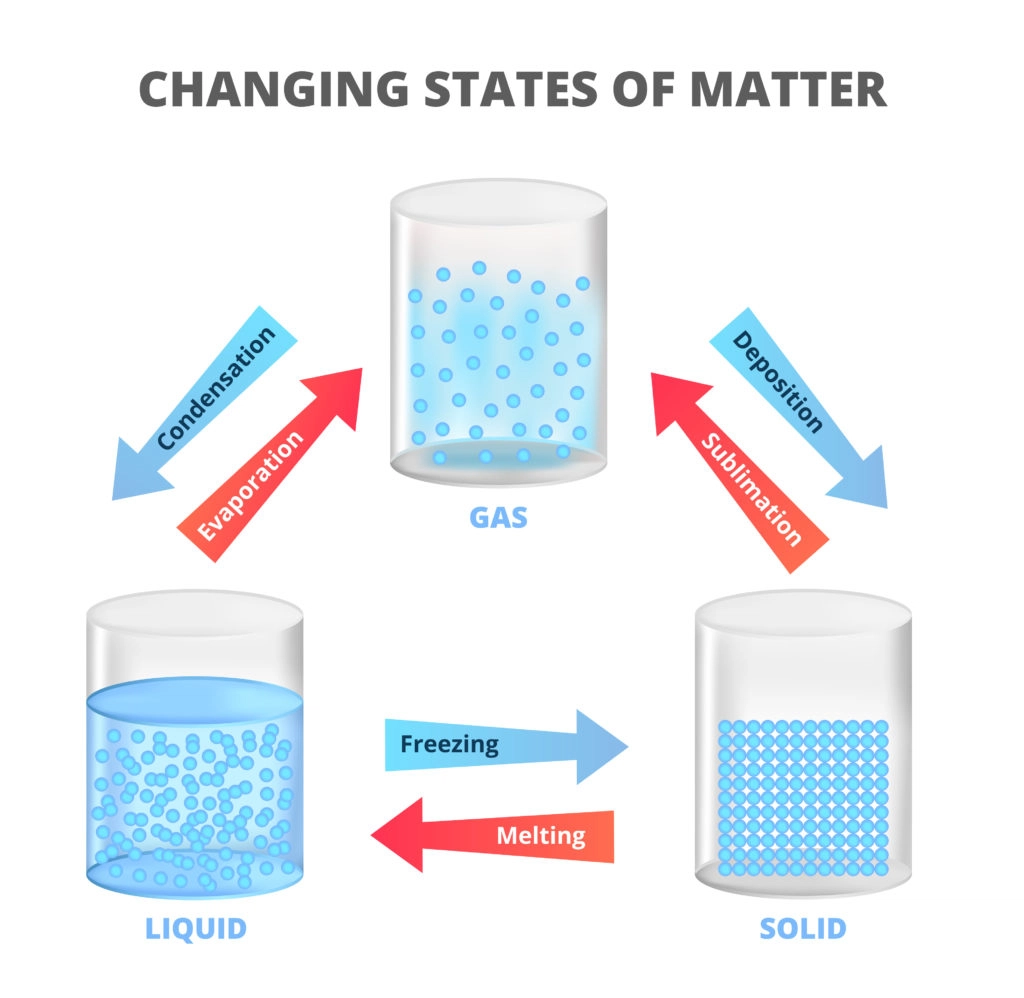
Exploring the Nature of Matter with CBSE NCERT Download
What is matter?
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It is one of the fundamental concepts in physics and is considered the substance of which physical objects are composed. Matter can exist in various forms, including solid, liquid, and gas, and it can undergo physical and chemical changes.
The basic building blocks of matter are atoms, which are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. These subatomic particles give matter its structure and properties. The arrangement and movement of these particles determine the state and behavior of different types of matter.
Nature of Matter
The nature of matter refers to the fundamental characteristics and properties of substances that make up the physical universe. Understanding the nature of matter involves exploring its structure, composition, and behavior at various levels, from the smallest particles to the grandest celestial bodies. Here are some key aspects of the nature of matter:
Atomic Structure:
Matter is composed of atoms, which are the basic building blocks. Atoms consist of a nucleus, made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in orbit.
States of Matter:
Matter exists in different states—solid, liquid, and gas—based on the arrangement and energy of its particles.
Elements and Compounds:
Elements are pure substances composed of only one type of atom, while compounds are composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
Chemical Reactions:
The nature of matter is dynamic, involving chemical reactions where substances can transform into different ones.
Forces and Interactions:
Matter interacts through various forces, including gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear forces.
Energy and Matter:
The relationship between matter and energy is a fundamental aspect of the nature of matter. Einstein's famous equation, E=mc².
Subatomic Particles:
Beyond atoms, the study of subatomic particles like quarks and leptons contributes to our understanding of the fundamental nature of matter and the forces that govern the universe.
Examples of Nature of Matter
Compound
Nature- Compounds are formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in fixed ratios.
Water (H₂O) is a compound composed of hydrogen and oxygen in a fixed ratio.
Element
Nature- Elements consist of identical atoms, each defined by a specific number of protons.
Gold is an element composed of gold atoms. Each gold atom has the same number of protons in its nucleus.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
|
1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary |
View Page / Download |
|
2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books |
View Page / Download |
|
3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions |
View Page / Download |
|
4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar |
View Page / Download |
|
5. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers |
View Page / Download |
|
6. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank |
View Page / Download |
|
7. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes |
View Page / Download |
|
8. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources |
View Page / Download |
|
9. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books |
View Page / Download |
|
10. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet |
View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES:
Q1 What is the nature of matter?
Answer. The nature of matter is characterized by its fundamental building blocks, which include atoms and molecules. Matter occupies space and has mass.
Q2 What are the three states of matter, and how do they differ?
Answer. The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. They differ in the arrangement and movement of particles. In solids, particles are closely packed and vibrate in fixed positions. Liquids have particles that can move past each other, and gases have particles that move freely and widely.
Q3 How do chemical changes differ from physical changes in matter?
Answer. Chemical changes involve the formation of new substances with different properties, while physical changes alter the state or form of a substance without changing its chemical composition.
Q4 How does matter interact with energy
Answer. Matter interacts with energy through various processes, such as absorbing or releasing heat, undergoing state changes (melting, freezing), and participating in chemical reactions where energy is either absorbed or released.
Q5 What distinguishes mixtures from solutions?
Answer. Mixtures are combinations of substances that retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means. Solutions, a type of mixture, are homogeneous mixtures where one substance (solute) is uniformly distributed in another (solvent) at a molecular level.

| CBSE CLASS 11th Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| > Importance of Chemistry |
| > Properties of Matter and their Measurement |
| > Uncertainly in Measurement |
| > Laws of Chemical Combinations |
| > Dalton's Atomic Theory |
| > Atomic and molecular Masses |
| > Mole Concept and Molar Masses |
| > Percentage composition |
| > Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| CBSE Class 11 Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |