CBSE Class 10th Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid Details & Preparations Downloads
Understanding the characteristics and uses of different compounds is crucial for both academic and practical knowledge in the field of chemistry. Two of these substances, ethanol, and ethanoic acid, are important in a variety of contexts, including daily life and business. In this blog, we examine the formulae, structures, characteristics, and practical applications of ethanol (C2H5OH) and ethanoic acid (CH3COOH).
The formula and structure of ethanol
Known by several names, including ethyl alcohol or just alcohol, ethanol is a multipurpose substance. Its molecular makeup, which consists of two carbon atoms (C), six hydrogen atoms (H), and one oxygen atom (O), is shown by its chemical formula, C2H5OH. The hydroxyl (-OH) functional group that is bonded to a carbon atom makes ethanol a member of the alcohol class.
Ethanol's structural formula provides a more vivid representation of its molecular structure. One carbon atom joins forces with three hydrogen atoms and one more carbon atom to create a single bond in ethanol. A linear molecule structure is produced when the remaining carbon atom makes a single bond with two hydrogen atoms and a bond with the hydroxyl group (-OH).
Properties of Ethanol
The following physical and chemical characteristics of ethanol lead to its widespread use:
Solubility: The solubility of ethanol in water allows it to dissolve in any amount since it is miscible with it. Because of this characteristic, it is a useful solvent in a number of sectors, including as the manufacturing of beverages, cosmetics, and medicines.
Flammability: Because of its great flammability, ethanol can be used as a fuel or as a component in fuel blends. Its flammable property makes it easier to employ in hand sanitizers with alcohol.
Boiling Point: At typical atmospheric pressure, ethanol has a comparatively low boiling point of 78.37°C (173.1°F). This characteristic makes it perfect for procedures involving distillation, such the creation of biofuels and alcoholic drinks.
Antiseptic Properties: Because of its antiseptic qualities, ethanol is useful for sanitizing surfaces and cleaning wounds. It causes microbes' proteins to become denatured, which upsets their cellular structures and makes them inert.
Examples of Ethanol in the Real World
Alcoholic Beverages: The main intoxicating ingredient in alcoholic beverages including wine, spirits, and beer is ethanol. Yeast ferments carbohydrates to produce carbon dioxide and ethanol, which gives these drinks their distinctively high alcohol level.
Biofuel Production: One renewable fuel source used in the manufacturing of biofuel is ethanol. It may be produced by methods like fermentation and distillation from biomass feedstocks including maize, sugarcane, and switchgrass. E10 or E85 gasoline is combined with ethanol to lower greenhouse gas emissions and raise fuel's octane rating.
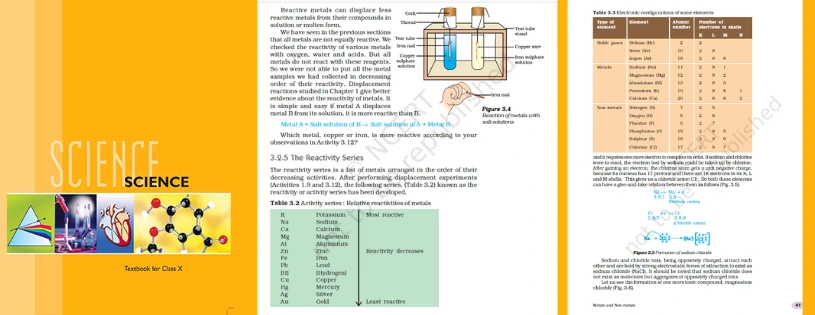
The formula and structure of ethanoic acid
With the molecular formula CH3COOH, ethanoic acid—also referred to as acetic acid—is a carboxylic acid. Two carbon, four hydrogen, and two oxygen atoms make up its molecular structure. The distinctive acidic qualities are defined by the carboxyl group (-COOH).
More information on the molecular structure of ethanoic acid may be found in its structural formula. Three hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom create single bonds and a double bond with one carbon atom, respectively. One oxygen atom, which is connected to another hydrogen
atom, and the second carbon atom create a single bond. The molecule is polar because of the oxygen atom's single pair of electrons that it shares with the second carbon atom.
Properties of Ethanoic Acid
Because of its molecular structure and acidic nature, ethanoic acid has certain characteristics.
Acidity: Ethanoic acid is a weak acid that partially dissociates to produce acetate (CH3COO-) and hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions. Compared to powerful mineral acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, its acidity is low.
Pungent Odor: Even in diluted solutions, ethanoic acid has a strong, vinegar-like smell. This particular scent is what gives vinegar, which is acetic acid in water, its unique fragrance.
Corrosiveness: When concentrated ethanoic acid comes into touch with some metals, it can corrode them and cause skin irritation. But compared to powerful mineral acids, its corrosive effects are less severe, which makes it safer for use in some industrial applications.
Solubility: When ethanoic acid is dissolved in water, acidic solutions are created. Its usage in food preservation, cooking, and chemical compound manufacturing all depend on this quality.

Examples of Ethanoic Acid in the Real World
Use in Cooking: Vinegar, which contains ethanol, is a common component in food preparation and cooking. It adds a zesty taste to food and is used as a preservative in pickling procedures.
Chemical Synthesis: A wide range of chemical substances, such as polymers, perfumes, and medicines, are synthesized using ethanoic acid as a precursor. It may take part in a number of chemical processes, including esterification and condensation, thanks to its functional groups.
Conclusion
Two examples of the many uses and significance of organic compounds in chemistry are ethanol and ethanoic acid. Although ethanol is useful as a fuel, solvent, and disinfectant, ethanoic acid has use in the industrial, pharmacological, and culinary fields. Our understanding of these compounds' structures, functions, and real-world applications is enhanced by our knowledge of their formulae, characteristics, and natural environments. There is no denying the importance of ethanol and ethanoic acid in influencing our lives and industries as we continue to investigate the complexities of organic chemistry.
CBSE Class 10 NCERT Science Topics for a Strong Foundation
| Chapter Name | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Topic Number | Topic Name |
| 4.1 | Covalent Bonding in Carbon Compounds |
| 4.2 | versatile nature of Carbon |
| 4.3 | Nomenclature of carbon Compounds |
| 4.4 | Differences Between Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
| 4.5 | Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid |
List of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Chapter 2 | Acids, Bases and Salts |
| Chapter 3 | Metals and Non-metals |
| Chapter 4 | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Chapter 5 | Life Processes |
| Chapter 6 | Control and Coordination |
| Chapter 7 | How do Organisms Reproduce? |
| Chapter 8 | Heredity |
| Chapter 9 | Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Chapter 10 | The Human Eye and the Colourful World |
| Chapter 11 | Electricity |
| Chapter 12 | Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| Chapter 13 | Our Environment |
List of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Real Numbers |
| Chapter 2 | Polynomials |
| Chapter 3 | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Chapter 4 | Quadratic Equations |
| Chapter 5 | Arithmetic Progressions |
| Chapter 6 | Triangles |
| Chapter 7 | Coordinate Geometry |
| Chapter 8 | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Chapter 9 | Some Applications of Trigonometry |
| Chapter 10 | Circles |
| Chapter 11 | Areas Related to Circles |
| Chapter 12 | Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 13 | Statistics |
| Chapter14 | Probability |
FAQs
Que1. What is Ethanoic acid used for?
Ans: Acetic acid is used to produce volatile organic esters, vinyl acetate, which is used to manufacture plastics, cellulose acetate, which is used to make textiles and photographic films, and metal acetates, which are used in various printing processes.
Que2. Is Ethanoic acid used to preserve food?
Ans: There are more uses for acetic acid outside salad dressing. In addition to being an active ingredient in edible films and hurdle preservation technology, it is used as a natural preservative and antibacterial agent in the preservation of food.
Que3. Is Ethanoic acid a vinegar?
Ans. Acetic acid, another name for ethanoic acid, is just ethanoic acid diluted with water. Nowadays, most ethanoic acid is produced synthetically and used to make other necessary chemicals like plastics.
Que4.Why is Ethanoic acid a weak acid?
Ans: Acetic acid, sometimes known as ethanoic acid, is categorized as a weak acid since it does not release all of its hydrogen in water. Rather, it partially dissociates and attains equilibrium with its conjugate base.
Que5.Why do esters smell sweet?
Ans: The ester that is created when ethanol and acetic acid combine has a pleasant scent. The esters have a little intermolecular contact with one another. Because the intermolecular force of attraction is smaller in ester molecules, they are naturally volatile. Esters do not also have hydrogen bonds.


.webp)

