CBSE Class 10th Basic Metallurgical Processes & Preparations Downloads
The crust of the planet contains a vast array of metals. Minerals are naturally occurring metallic compounds with a specific chemical composition that are combined with sand, soil, and rocks. Ore is a metallic complex with a reasonably high metal content that may be economically and conveniently utilized to separate certain components.
The definition of metallurgy is the area of chemistry concerned with the extraction of pure metal from its ore.
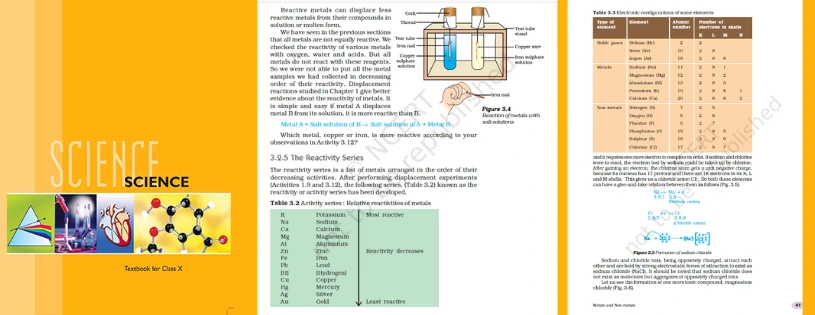
Metallurgy Process
Metals are refined and alloys made of metals are produced during the metallurgy process. Gangue is the term for the impurities found in ore that must be removed during the extraction process in order to recover the desired metal from the ore. Flux is a material that is added to the furnace in order to eliminate the gangue that is contained in the ore.
The following are the main procedures in metal metallurgy:
1. the ore's crushing and grinding
2.Concentration of the mineral
3.Removal of the unfinished metal
4.The metal's purification
Fundamentals of Metallurgy
The ore's crushing and grinding: Pulverization, or the crushing of ores into fine powder in a crusher, is the main step in the metallurgy of metals.
The Ore Concentration: The earth's crust is mined for its ores, which are combined with a variety of undesirable impurities known as gangue, including mica, quartz, silicates, sand, feldspar, and quartz. Dressing is the process of removing these undesirable contaminants from the ore. Because it progressively raises the proportion of metal in the ore, the dressing of ore is also known as the concentration of the ore. In metallurgy, the following techniques are used to obtain ore concentration:
Physical Methods: The old-fashioned way of gathering ore by hand is called hand-picking. With the use of a hammer, the ore is separated from the gangue or adhering stony components in this procedure.
Hydraulic Method: Levigation, gravity separation, or hydraulic method: Based on the variations in the masses of the ore and gangue particles that are present in the ore, this technique is a gravity separation method used in metallurgy. When the ore particles are larger in bulk than the rocky gangue particles, this technique is commonly applied. It is employed to concentrate lead, tin, iron, and other heavy oxide ores.
With this technique, the powdered ore is mixed using water jets in a hydraulic classifier, also called a Wilfley table, which causes the heavier ore particles to sink to the bottom and removes the lighter impurities. This process concentrates the oxides and carbonate ores. This process, also known as levigation, is used for iron, gold, chromium, and other metals.
Magnetic separation: When there is a magnetic nature present in the impurities or the ore, this metallurgical process is employed. For instance, the magnetic characteristics of the ore and gangue particles differ in magnetic ores such as pyrolusite (MnO4) and chromite (FeO.CrO₃). Using this approach, a conveyor belt that revolves around two wheels and passes over a magnetic roller carries the ground ore. The mixture's magnetic particles are drawn to the magnetic wheel, which also helps to separate them from the non-magnetic particles.
Froth floatation: To separate sulfide ores, crushed ore is combined with a solution of water, detergent, and pine oil in a tank. Froth is created when compressed air is forced through an agitator's revolving pipe. The ability to distinguish between the gangue particles and the ore's wetting characteristics aids in their separation. The sulfide ore particles float up with the lighter froth because the pine oil covers and wets them. The gangue particles descend to the bottom of the tank after being moistened by the heavy water. After being moved to a new container, the froth containing the sulfide ore is cleaned and dried.
Chemical Method
Leaching: An appropriate solvent can be used to treat ores chemically through a process called leaching. In leaching, certain chemicals are used to treat the powdered ore, dissolving the ore but leaving the undesirable impurities behind. Filtration is used to get rid of the undissolved contaminants.
For instance, the aluminum ore bauxite (Al2O4) includes silica, titanium oxide, and ferric oxide—unwanted impurities. At between 1500 and 1700 degrees Celsius, an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is applied to the finely ground bauxite ore. The alumina (Al3O4) in the ore is dissolved by NaOH to create soluble meta aluminate; the other oxides (Fe3O4), TiO₃, and SiO₃) are insoluble and must be filtered out.
2NaAl(OH)₄(aq) is produced by Al₂O₃.2H₂O (s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H₂O (l).
Hydrated sodium aluminate
xHO(s) + 2 NaHCO₃ + 2NaAl(OH)₄(aq) → Al₂O₃.
The remaining sodium silicate in the solution precipitates out as hydrated alumina, which is then separated using the filtering technique. After that, it is heated to 1470 K, which produces pure alumina, to dry it.
xH₂O (s) -> Al₃O₃ (s) + xH₂O
We refer to this procedure as Baeyer's process.
Roasting: Roasting is the process of vigorously heating a concentrated ore at a temperature below the metal's melting point when there is an abundance of oxygen present. For sulfide ores, this procedure is frequently employed.
2SO₂ + 2ZnO -> 2ZnS + 3O₂
During Roasting:
1.Oxides are partially produced from sulfides.
2.Volatile contaminants are eliminated
Sulfur (SO₃), arsenic (As₃O₃), and antimony (Sb₃O₃) are eliminated as free elemental forms.
Calcination: Calcination is the process of heating a concentrated ore without air to melt the ore. The carbonate ores are processed in this manner.
ZnO + CO₂ -> ZnCO₃
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Al + 2H + O → Al + O + O
While the material is being calcined:
During calcination:
1.Moisture is eliminated
2.Porous mass is created.
3.Volatile contaminants are eliminated
4.Carbonate ores break down into oxides.
5.The hydrated oxide ore's water is eliminated.
Various types of furnaces are used for roasting and calcination; the reverberatory furnace is the most often utilized type. The air holes are either completely or partially blocked during the calcination process, but they are always maintained open during the roasting phase.
CBSE Class 10 NCERT Science Topics for a Strong Foundation
| Chapter Name | Metals and Non-metals |
| Topic Number | Topic |
| 3.1 | Properties of Metals and Non-metals |
| 3.2 | Reactivity Series |
| 3.3 | Formation and Properties of Ionic Compounds |
| 3.4 | Basic Metallurgical Processes |
| 3.5 | Corrosion and its Prevention |
List of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Chapter 2 | Acids, Bases and Salts |
| Chapter 3 | Metals and Non-metals |
| Chapter 4 | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Chapter 5 | Life Processes |
| Chapter 6 | Control and Coordination |
| Chapter 7 | How do Organisms Reproduce? |
| Chapter 8 | Heredity |
| Chapter 9 | Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Chapter 10 | The Human Eye and the Colourful World |
| Chapter 11 | Electricity |
| Chapter 12 | Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| Chapter 13 | Our Environment |
List of CBSE Class 10 Mathmetics Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Real Numbers |
| Chapter 2 | Polynomials |
| Chapter 3 | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Chapter 4 | Quadratic Equations |
| Chapter 5 | Arithmetic Progressions |
| Chapter 6 | Triangles |
| Chapter 7 | Coordinate Geometry |
| Chapter 8 | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Chapter 9 | Some Applications of Trigonometry |
| Chapter 10 | Circles |
| Chapter 11 | Areas Related to Circles |
| Chapter 12 | Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 13 | Statistics |
| Chapter14 | Probability |
CBSE Class 10th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 10th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 10th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 10th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 10th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 10th Last Minutes Preparation Resources (LMP) | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 10th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 10th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
FAQs
Que1. .What is metallurgy?
Ans. The study and technique of removing metals from their ores, purifying them, and forming them into functional items is known as metallurgy.
Que2.How is metallurgy used for production?
Ans. Metallurgy is used in manufacturing processes to extract, purify, and work with metals, making it possible to make a wide range of items, from electrical equipment to automobiles.
Que3.What is the history of metallurgy?
Ans. The discovery of metals like copper and gold approximately 6000 BCE marked the beginning of thousands of years of metallurgy's history. As a result of early civilizations' ability to collect and use these metals, substantial advances in metalworking skills were made throughout the Bronze Age (3300–1200 BCE) and Iron Age (1200 BCE onward). Metallurgy developed with human civilization, influencing advancements in both technology and the economy across time.
Que4.Write an note on metal and its alloys?
Ans. Materials used in engineering and production are metal and its alloys. In addition to their malleability and ductility, metals are known for their capacity to carry heat and electricity. Alloys are composed of two or more metals mixed with non-metallic components to improve characteristics like conductivity, strength, and resistance to corrosion. Because of their adaptability and adjustable qualities, they are essential to a wide range of sectors, from electronics to construction.
5.What is extractive metallurgy?
Ans. The area of metallurgical engineering known as extractive metallurgy is dedicated to the extraction of metals from their ores and their subsequent refinement into products that are useful.


.webp)

