CBSE Class 10th Versatile Nature of Carbon & Preparations Downloads
The fact that carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds helps to explain its versatile character. It can also form rings, branches, and chains when joined to other carbon atoms. The Latin word "carbo," meaning charcoal, is the source of the English word "carbon," which is present in many different chemical compounds, including those found in space. We will examine carbon's versatility in this post.
What Does Carbon's Versatile Nature Mean?
Because carbon atoms are unique, there are an endless number of carbon compounds in the natural world. Its tetravalent and catenation properties allow it to produce a wide variety of compounds.
Basically, carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and a few other atoms combine to produce organic molecules. But unlike any other element, carbon has the power to produce a vast range of compounds because of its inherent nature. One specific topic on the versatile nature of carbon is mentioned in the chapter Carbon and its Compound. We'll talk about the same subject today and examine the key traits of the element carbon and its many applications.
Explanation: Versatile Nature of Carbon
There are two forms of carbon found in nature: the free state and the compound state. It exists as diamond, graphite, and Buckminster fullerene in its free state. These substances exclusively include carbon, which explains why their chemical characteristics are comparable. But because of the different ways that carbon atoms form, they look different from one another. They go by the name "carbon allotropes" as well.
In contrast, carbon forms bonds with other elements to form new compounds while it is in the compound state. They could be in the form of a solid, a liquid, or even a gas. A vast array of organic compounds are formed as a result of carbon's ease with which it can make bonds with other atoms.
A recent estimate places the approximate number of chemical formulas for carbon that are currently known at 3 million. This is far more than the total number of compounds created by combining all other elements.
Reasons for the Versatile Nature of Carbon
The versatile nature of carbon can be better explained by the salient features of this element. The specific features of a carbon atom are given below.
Catenation
Carbon atoms show this property, according to which they can form bonds by self-linking to other carbon atoms.
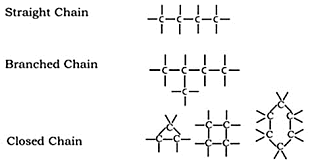
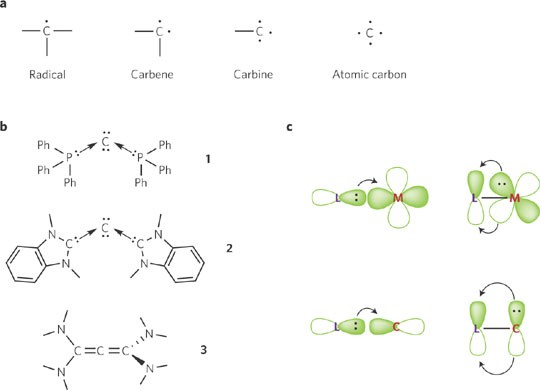
(i) Carbon's catenation characteristic forms far more stable compounds than other compounds. As a result, many different carbon compounds are formed as long chains, branched chains, and rings.
(ii) Through self-linking, carbon atoms can create single, double, or triple bonds. Saturated compounds are those made up of a single bond, such as methane (CH4). Unsaturated compounds are carbon compounds that have two or three bonds between the carbon atoms; alkene (C2H4) has two bonds, and ethyl (C2H2) has three bonds.
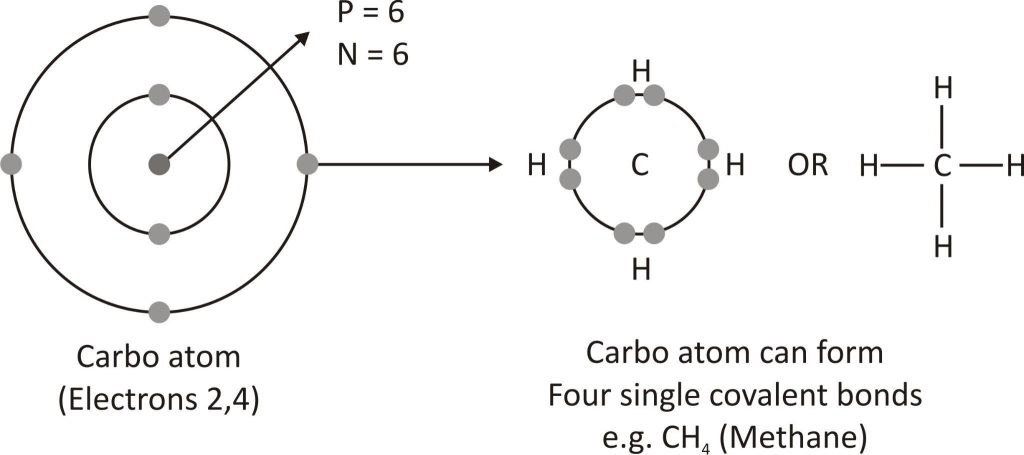
Tetravalency
Atoms of carbon have a valency of 4. It shares its valence shell electrons with other elements to create covalent bonds since it is unable to obtain or lose four electrons in order to complete its octet. With hydrogen, oxygen, chlorine, nitrogen, etc., carbon forms covalent bonds to produce a variety of compounds.
Isomerism
Isomerization is seen in carbon compounds. Compounds with distinct chemical structures but the same or similar chemical formula are known as isomers. Because of the different configurations of the carbon atoms, this phenomenon is primarily observed in carbon compounds. In carbon compounds, structural isomerism is exemplified by the three isomers of pentane (C5H12).

Conclusion
The characteristics that make a carbon atom the most adaptable element in the periodic table are its tetravalency, isomerism, and catenation. The vast number of compounds that carbon atoms can create is due to each of these characteristics. Since inorganic compounds don't form bonds, their number is far smaller than that of organic compounds.
CBSE Class 10 NCERT Science Topics for a Strong Foundation
| Chapter Name | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Topic Number | Topic Name |
| 4.1 | Covalent Bonding in Carbon Compounds |
| 4.2 | versatile nature of Carbon |
| 4.3 | Nomenclature of carbon Compounds |
| 4.4 | Differences Between Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
| 4.5 | Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid |
List of CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Chapter 2 | Acids, Bases and Salts |
| Chapter 3 | Metals and Non-metals |
| Chapter 4 | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Chapter 5 | Life Processes |
| Chapter 6 | Control and Coordination |
| Chapter 7 | How do Organisms Reproduce? |
| Chapter 8 | Heredity |
| Chapter 9 | Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Chapter 10 | The Human Eye and the Colourful World |
| Chapter 11 | Electricity |
| Chapter 12 | Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| Chapter 13 | Our Environment |
List of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Chapter
| Chapter Number | Chapter Name |
| Chapter 1 | Real Numbers |
| Chapter 2 | Polynomials |
| Chapter 3 | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Chapter 4 | Quadratic Equations |
| Chapter 5 | Arithmetic Progressions |
| Chapter 6 | Triangles |
| Chapter 7 | Coordinate Geometry |
| Chapter 8 | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Chapter 9 | Some Applications of Trigonometry |
| Chapter 10 | Circles |
| Chapter 11 | Areas Related to Circles |
| Chapter 12 | Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter 13 | Statistics |
| Chapter14 | Probability |
FAQ-
Q.1: What makes carbon so versatile?
Ans. carbon's versatility stems from its ability to form four strong covalent bonds with other atoms, including other carbon atoms, enabling it to create a vast array of molecular structures.
Q.2: How does carbon's ability to form bonds contribute to its versatility?
Ans. Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds with other atoms, allowing for the creation of a diverse range of organic compounds with varying properties.
Q.3: What are some examples of carbon's versatility in nature?
Ans. Carbon can form the backbone of complex biological molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for life. Additionally, carbon-based materials such as diamonds and graphite showcase their versatility in physical properties.
Q.4: Can you explain carbon's role in climate change?
Ans. Carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas produced from burning fossil fuels, contributes to climate change by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere. Understanding carbon's behavior in the environment is crucial for mitigating climate change.
Q.5: What are some emerging applications of carbon-based materials?
Ans. Carbon nanotubes, graphene, and other carbon allotropes hold promise for various applications such as nanotechnology, energy storage, and biomedical devices, showcasing ongoing exploration of carbon's versatility.



